Biological large-scale model reaches new milestone!
On February 20th, scientists from the Arc Institute, NVIDIA, Stanford University, the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of California, San Francisco, jointly released the large biological model Evo 2.

According to the team, Evo 2 is the largest public AI biological model to date, with the full version having up to 40 billion parameters and containing 9.3 trillion nucleotides from 128,000 species.
It encompasses the basic languages of biology: DNA, RNA, and proteins, and is capable of analyzing sequence lengths up to a million nucleotides at a time.
As a basic model of the genome, it has the ability to generate the entire genome, predict mutations, and understand non-coding DNA. It can be widely used in biomolecule research, precision medicine, drug development, synthetic biology, etc.
In addition, Evo 2 is one of the largest and most comprehensive open-source models in the field of biology. Its release includes training data, training and inference code, as well as model weights, which has set off a sensation in the academic community.
This also means that humans have the ability to rewrite the lowest code of life - the genome, which will open the door to a new era of biotechnology.
01 Evo 2 is shockingly released with multiple upgrades
If DeepSeek is based on text as a large model, then Evo 2 is based on genomic data, but it does not generate text, but a genome sequence.
In the first generation of Evo, scientists used the genomes of 80,000 bacteria and archaea, where they were trained at single-nucleotide resolution, enabling their models to complete genome-wide scale prediction tasks and generative design.
Evo 2 has undergone major upgrades in all aspects, and its overall capabilities have also made a huge leap.
First of all, the amount of data in Evo 2 is huge. The full version contains 40 billion parameters, far exceeding the 7 billion parameters of the first generation. Evo 2 was trained on the genomes of 128,000 species, including humans and other animals, plants, and other eukaryotes, containing a total of 9.3 trillion nucleotides.
Secondly, Evo 2 uses StripedHyena 2 as the model architecture. Different from the current common transformer architecture, it can not only respond faster, but also capture genome interactions, autonomously learn exon-intron boundaries, and transcription factor binding sites and other information.
Evo 2 significantly expands the context window and can process up to 1 million base pairs at a time. This large-scale processing capability is very important for genomes because it helps process long sequences in the genome and also means a major advance in computational biology.
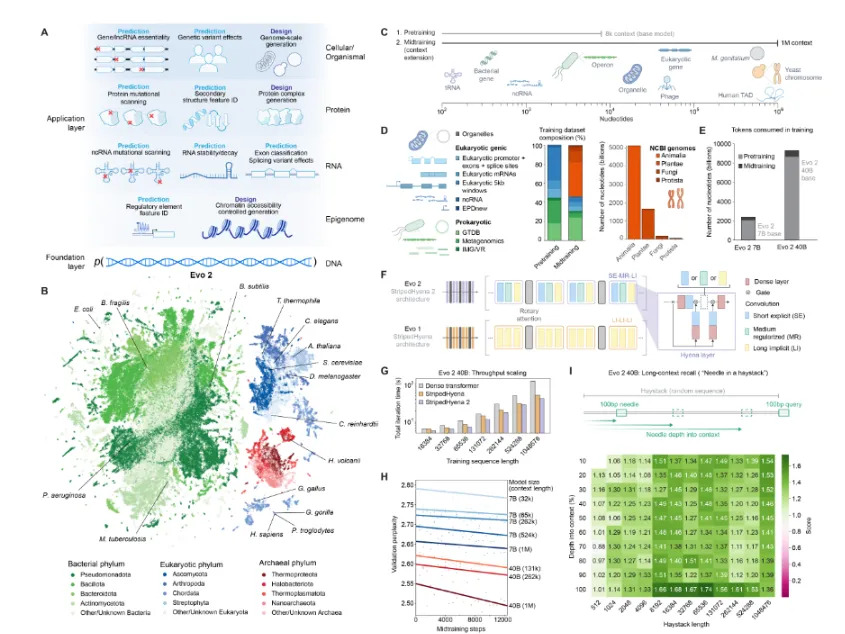
For downstream tasks, Evo 2 can perform general prediction and design tasks across DNA, RNA and proteins. Previously Evo 1 generated the world's first artificial intelligence-generated CRISPR-Cas system, a large functional complex of proteins and ncRNA (non-coding RNA).
Using Evo 2, researchers created yeast chromosomes, human mitochondrial genomes, and the prokaryotic genome of Mycoplasma genitalium (commonly used minimal genome models), proving its generation capabilities.
In addition, Evo 2 is also good at identifying disease-causing mutations in human genes, and can even deeply understand and identify genetic sequence patterns in different organisms that would take experimental researchers years to discover.
On a technical level, training up to 40 billion parameters at nucleotide accuracy is not easy, and even OpenAI co-founder and president Greg Brockman spent time on the problem during his vacation.
In the end, it was Jensen Huang who came forward to support the project. Officials stated that Evo 2 was trained on the NVIDIA DGX Cloud AI platform and used more than 2,000 H100 GPUs. Ultimately, Evo 2 was able to use 30 times more data for training than Evo 1, and the number of nucleotides inferred at one time was more than 8 times that of Evo 1.
Of course, the result is that Evo 2 is integrated into NVIDIA BioNeMo and becomes a member of NVIDIA’s family of life science models.
The project is completely open source, and the research team has uploaded its training data, training and inference codes, and model weights on github. It is the largest open source biological AI model to date.
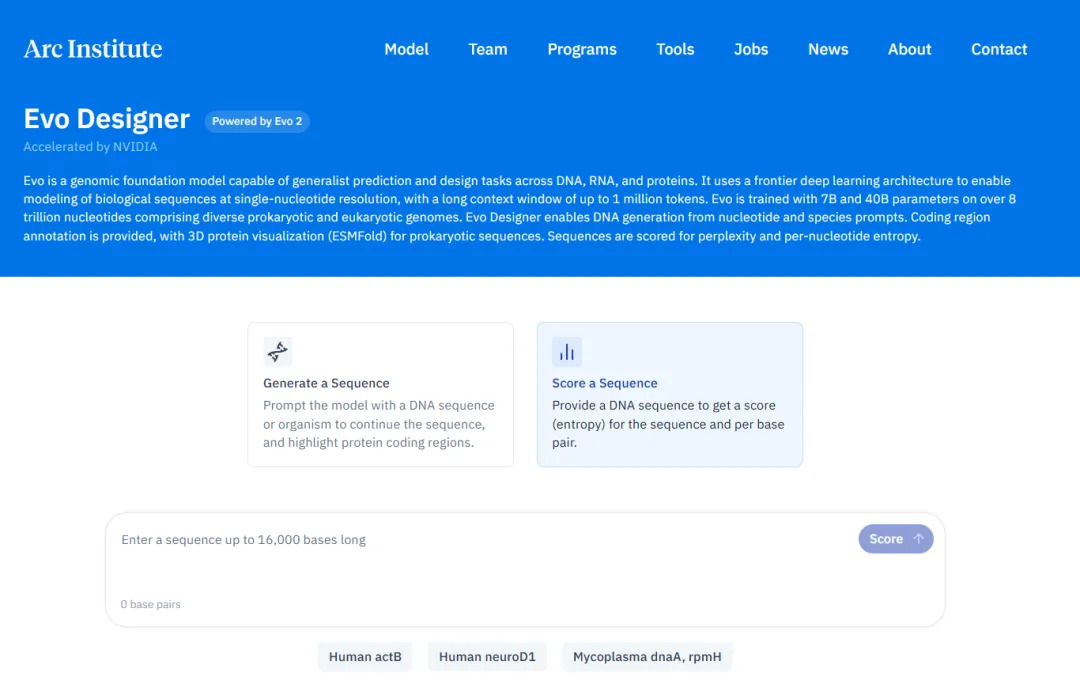
In addition, the researchers also developed an online AI platform called Evo Designer. Scientists can input genome sequences and perform genome generation and prediction in this platform, which is really very considerate.
02 From genome to life
Patrick Hsu, co-founder of the Arc Institute and assistant professor at UC Berkeley, said the development of Evo 2 is an important breakthrough in the field of generative biology. Through this technology, machines can "read", "write" and "think" the language of nucleotides, driving progress in biological research. Evo 2’s training capabilities are comparable to large-scale language models, showing strong potential in predicting disease mutations and designing potential artificial life.
In short, Evo 2 has learned the basic principles of DNA, marking a revolutionary advancement of AI in biology, and is expected to open up a vast world for precision medicine, drug development, and synthetic biology.
Precision Medicine
Evo 2 can accurately identify the association between gene mutations and diseases without requiring special training on human disease data. Its performance in mutation prediction even exceeds that of models specifically targeting this gene. For example, in the variant test of the breast cancer-related gene BRCA1, Evo 2’s accuracy in predicting mutations exceeds 90%. In the future, Evo 2 can conduct in-depth analysis of patient genomic data to support personalized medicine.
Drug Development
Evo 2 can not only interpret gene sequences, but also design new genomes and biomolecules (such as protein molecules, etc.). This means researchers can use the model to design new drug molecules against specific disease targets.
In the field of gene therapy, Evo 2 can design genetic elements that are only activated in specific cell types, such as new transposons or gene switches, to improve the safety of gene therapy by mitigating off-target effects. In the future, Evo 2 is expected to be able to find the genetic causes of human diseases and accelerate the development of new drugs, reducing the time and research funds required for cell or animal experiments.
Synthetic Biology
For Evo 2, synthetic biology is a broader field.
By generating new DNA sequences, Evo 2 can design organisms with special properties to fill ecological niches that do not exist in nature. For example, Evo 2 can design proteins that break down plastic, or microorganisms that improve the climate. In the agricultural field, Evo 2 is also expected to solve the global food shortage problem and deepen scientists' understanding of plants.
Scientists also considered potential ethical and safety risks.
Pathogens that infect humans and other complex organisms have been excluded from Evo 2's base data set, ensuring that the model does not generate valid answers to such questions.
Simply put, AI is no longer limited to describing biology, but starting to design biology, making possible synthetic life designed from scratch, programmable genomes optimized by AI, potential new gene therapies, and even laying the foundation for virtual cells.
Evo 2 is completely open source, which may also trigger large-scale innovation in the field of bioengineering and reduce the huge obstacles to genome design.
But like the General Basic Large Model, it remains to be seen where the Evo 2 can make the biggest impact. Unlike small models that perform specific tasks, researchers may also need to build task-specific AI programs on top of the models.
The Arc Institute, the creators behind Evo 2, also demonstrated a more ambitious goal: to simulate the entire cell.
Evo 2 is expected to combine genomic data with various types of data such as epigenetics and proteomics, which also means implementing larger-scale life programming.
Maybe in the future, we may actually see AI create new life forms.















